Vaginal pH is one of the key parameters’ for optimal health and wellness of women.
Simply put – Vaginal pH means the acidity maintained and to be critically maintained in the vagina for prevention of infections.
Normal, healthy women have ACIDIC pH and the normal range of vaginal pH is 3.8 to 4.5 but even more preferrable range is 3.8 to 4.2 for optimal women’s health
It is increasingly realized that Vaginal pH Values serve as an early and inexpensive indicator for potential health problems.
The common vaginal microbiome, the Lactobacilli species, can produce acidic pH and bacteriocins to kill other bacteria in the vagina.
Lactobacilli can produce an acidic environment in the vagina, which is designed to protect women from sexually transmitted pathogens and opportunistic infections.
Vaginal Microflora Imbalance

- Mucosal colonization
- Preservation of mucus
- Competition for epithelial cell attachment sites
- Competition for nutrients
- Mucosal colonisation
- Mucus damage caused by glycosidase- producing anaerobes
- Adhesion to epithelial cells
- Production of antimicrobial substances
- Lactic acid, H O , bacteriocins, etc.
- Production of Noxious substances
- Polyamines, etc
- Immuno-modulation
- Inflammatory immune response
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1b and IL-6
*most common vaginal infection with incidence varying from 25-30% globally including pregnant women (CDC)
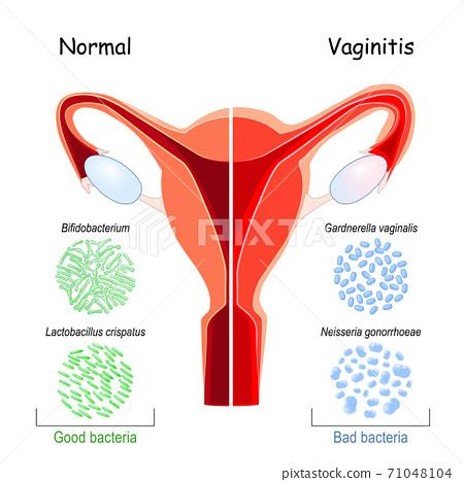
If these normal flora such as Lactobacilli are absent or significantly reduced, the vaginal ecosystem becomes imbalanced, and other microorganisms or bacteria inside vagina become overgrown, leading to a condition called vaginitis.
Vaginitis has different types, including bacterial vaginosis (BV), vaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis, and aerobic vaginitis
Vaginitis - Bacterial Vaginosis
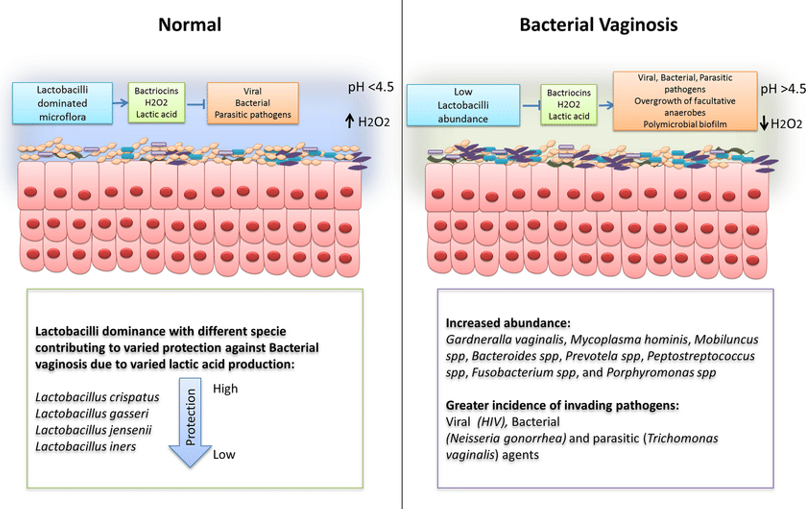
In today’s world, 75% of all women worldwide have had vaginitis at least once in their lives. The vagina has a dynamic microbial ecosystem with varying vaginal pH levels. An imbalance in that ecosystem can alter the vaginal pH and tip the scale to the point of causing issues, such as vaginitis, that require medical attention.
Importance of Normal Vaginal Microflora along the reproductive cycle !!!!
BEFORE
- STD, PID, RTIs
FERTILIZATION
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines
- Sperm motility and viability
PREGNANCY
- Amniotic fluid infection
- Chorioamnionitis, Late miscarriage
- Premature rupture of the membranes
- Virus reactivation (Cytomegalovirus, HSV)
AFTER
- Neonatal infection
Mastromarino et al., Ind J Med Res, 2014
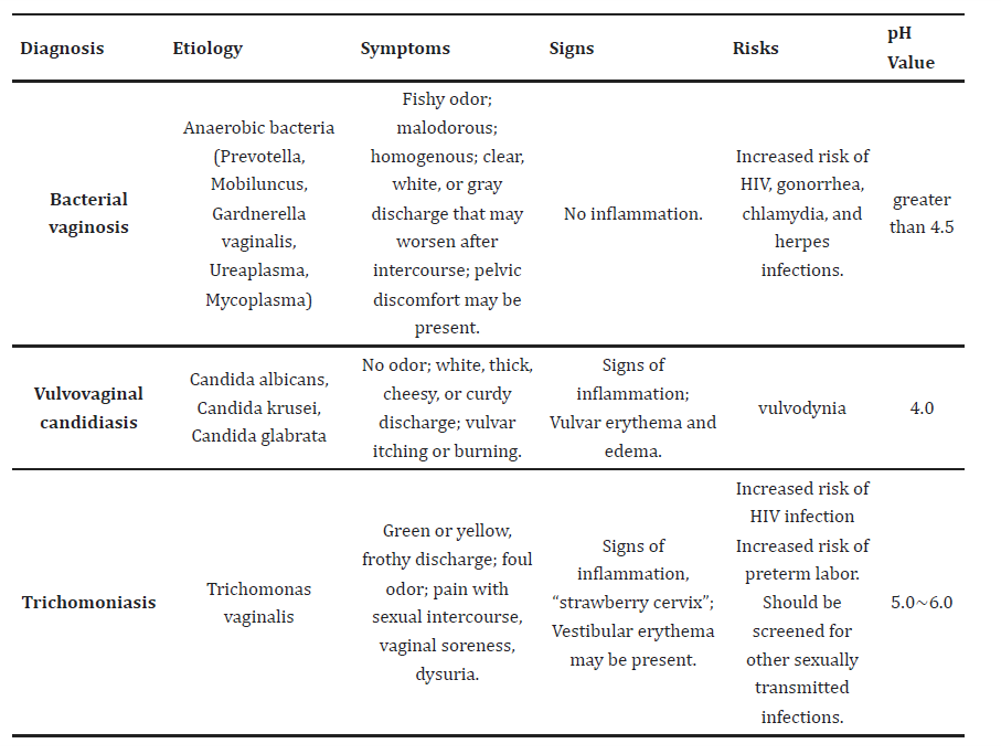
Most Common Types of Vaginitis and Symptoms
Association with INFERTILITY; META-ANALYSIS
Every 1 in 5 infertile women suffers from BV.
Nearly 40% infertile women show signs of BV-related abnormal microflora.
Evidence
BV Stacks the Odds in Favour of Infertility
The Odds
Prevalence of BV are 3.3. times higher among infertile women
In tubal infertility, its 2.7 times higher
Preclinical Pregnancy Loss are 2.3 times higher with BV
Noortje van Oostrum et al. Risks associated with bacterial vaginosis in infertility patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Human Reproduction, Volume 28, Issue 7, July 2013, Pages 1809–1815

NextGen Pharma is conducting clinical trials to assess the efficacy of Flora-Balance in the treatment of Infertility and Improving Outcomes of IVF*
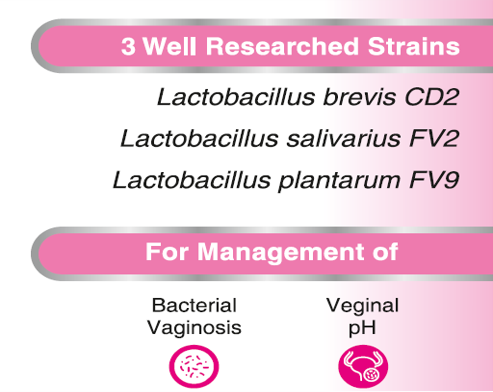
FloraBALANCE® contains 3 Well Researched, Live Strains of: